Qilum is a statistical and utility library supplementing existing statistical libraries, including numpy and scipy. We use numba library to speed up some calculations.
In this first version, we provide several random number generators. They are based on the C++ LOPOR library and the article Canonical local algorithms for spin systems: heat bath and Hasting’s methods. We respect the scipy.stats random number generator interface and any of the scipy.stats classes can be used to initialize qilum classes.
Example: Discrete Walker distribution
Dist_walker
# Define a discrete distribution with Walker algorithm
import qilum.stats as qs
walker = qs.Dist_walker(probabilities=[0.2, 0.5, 0.3], values=[0, 10, 2])
# and call the random number generator
rans = walker.rvs(size=100000)
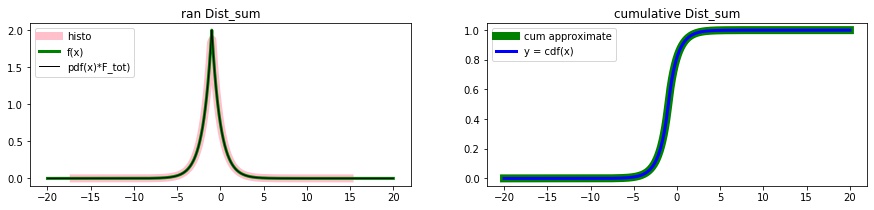
Example: Sum of distributions
Dist_sum
# exponential distributions left and right types
exp_left = qs.Dist_scale(scipy.stats.expon(),loc_x=-1.000001, scale_x=-1, scale_y=2, name='Exp+')
exp_right = qs.Dist_scale(scipy.stats.expon(),loc_x= -1, scale_x= 1, scale_y=2, name='Exp-')
# sum of the distributions
dist_sum = qs.Dist_sum([exp_left, exp_right]);
# random numbers
rans = dist_sum.rvs(100)
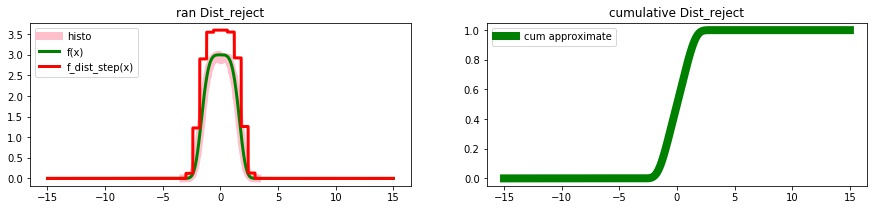
Example: Rejection method distribution
Dist_reject
# generate a random generator for f_f(x)
def f_f(xs): return np.where((xs<-5) | (xs>5), 0, 3.*np.exp(-np.power(xs,4)/10.))
# find a step function above f_f(x)
xs = np.linspace(-6,6, 1001)
ys = f_f(xs)
xs_step, ys_step = qs.f_max(xs, ys, 20)
ys_step *= 1.2 # just to be sure that our step function >= f_f()
# create a distribution for this step function:
hist_dist = scipy.stats.rv_histogram((ys_step, xs_step))
# scale this diribution
cumulative = qs.f_cumulative(xs_step, ys_step)[-1]
dist_step = qs.Dist_scale(hist_dist, scale_y = cumulative, name='dist_step')
# create dist_reject
dist_reject = qs.Dist_reject(dist_step, f_f)
# random numbers
rans = dist_reject.rvs(100)
The main classes are:
Dist_reject. Construct an exact generator for any probability functions. This is the fastest method when you do not know how to calculate or inverse the cumulative.Dist_sum. Construct a sum of known distributionsDist_scale. Apply scaling for x and y, for any distributions, even negative scaling for xDist_cubicSpline. Create an approximate random number generator for any functions using cubic spline. If you need an exact random number generator, useDist_reject. TheDist_cubicSplinecan be used instead of scipy.stats.rv_histogram if you need a smooth functionDist_walker. Create a very fast random number generator for discrete distributions.In addition, we expose the function
f_walker()which calculates the parameters of the Walker algorithm
stats Module¶
Functions¶
|
cumulative calculation |
|
maximun value ys in N intervals |
|
given N probabilities , return a series of N boxes of value mean(probabilities) with 2 indices in each. |
Classes¶
|
Distribution for (x,y): cubic splaine approximation for both cumulative ans values |
Base class for any qilum distribution |
|
|
Distribution with rejection method. |
|
Distribution scale for x and y: f_new = scale_y*f((x-loc_x)*scale_x) |
|
Distribution for a sum of distributions. |
|
Fast generator for discrete values using the Walker algorithm |